a. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infections
1) Code only confirmed cases
Code only confirmed cases of HIV infection/illness. This is an exception
to the hospital inpatient guideline Section II, H.
In this context, “confirmation” does not require documentation of
positive serology or culture for HIV; the provider’s diagnostic statement
that the patient is HIV positive or has an HIV-related illness is sufficient.
2) Selection and sequencing of HIV codes
(a) Patient admitted for HIV-related condition
If a patient is admitted for an HIV-related condition, the principal
diagnosis should be B20, Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV]
disease followed by additional diagnosis codes for all reported
HIV-related conditions.
(b) Patient with HIV disease admitted for unrelated condition
If a patient with HIV disease is admitted for an unrelated
condition (such as a traumatic injury), the code for the unrelated
condition (e.g., the nature of injury code) should be the principal
ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding andReporting
FY 2022
Page 20 of 115
diagnosis. Other diagnoses would be B20 followed by additional
diagnosis codes for all reported HIV-related conditions.
(c) Whether the patient is newly diagnosed
Whether the patient is newly diagnosed or has had previous
admissions/encounters for HIV conditions is irrelevant to the
sequencing decision.
(d) Asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus
Z21, Asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus [HIV]
infection status, is to be applied when the patient without any
documentation of symptoms is listed as being “HIV positive,”
“known HIV,” “HIV test positive,” or similar terminology. Do
not use this code if the term “AIDS” or “HIV disease” is used or
if the patient is treated for any HIV-related illness or is described
as having any condition(s) resulting from his/her HIV positive
status; use B20 in these cases.
(e) Patients with inconclusive HIV serology
Patients with inconclusive HIV serology, but no definitive
diagnosis or manifestations of the illness, may be assigned code
R75, Inconclusive laboratory evidence of human
immunodeficiency virus [HIV].
(f) Previously diagnosed HIV-related illness
Patients with any known prior diagnosis of an HIV-related illness
should be coded to B20. Once a patient has developed an
HIV-related illness, the patient should always be assigned code
B20 on every subsequent admission/encounter. Patients
previously diagnosed with any HIV illness (B20) should never be
assigned to R75 or Z21, Asymptomatic human
immunodeficiency virus [HIV] infection status.
(g) HIV Infection in Pregnancy, Childbirth and the Puerperium
During pregnancy, childbirth or the puerperium, a patient
admitted (or presenting for a health care encounter) because of an
HIV-related illness should receive a principal diagnosis code of
O98.7-, Human immunodeficiency [HIV] disease complicating
pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium, followed by B20 and
the code(s) for the HIV-related illness(es). Codes from Chapter
15 always take sequencing priority.
Patients with asymptomatic HIV infection status admitted (or
presenting for a health care encounter) during pregnancy,
childbirth, or the puerperium should receive codes of O98.7- and
Z21.
ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding andReporting
FY 2022
Page 21 of 115
(h) Encounters for testing for HIV
If a patient is being seen to determine his/her HIV status, use
code Z11.4, Encounter for screening for human
immunodeficiency virus [HIV]. Use additional codes for any
associated high-risk behavior, if applicable.
If a patient with signs or symptoms is being seen for HIV testing,
code the signs and symptoms. An additional counseling code
Z71.7, Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] counseling, may
be used if counseling is provided during the encounter for the
test.
When a patient returns to be informed of his/her HIV test results
and the test result is negative, use code Z71.7, Human
immunodeficiency virus [HIV] counseling.
If the results are positive, see previous guidelines and assign
codes as appropriate.
(i) History of HIV managed by medication
If a patient with documented history of HIV disease is
currently managed on antiretroviral medications, assign code
B20, Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] disease. Code
Z79.899, Other long term (current) drug therapy, may be
assigned as an additional code to identify the long-term
(current) use of antiretroviral medications.
Guideline C20 A 6
6) External cause code can never be a principal diagnosis An external cause code can never be a principal (first-listed) diagnosis.
The proper sequencing for HIV depends on the reason for the admission or encounter. When a patient is admitted for an HIV-related condition, sequence B20 Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] disease first, followed by additional diagnosis codes for all reported HIV-related conditions. Conditions always considered HIV-related include Kaposi’s sarcoma, lymphoma, Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), cryptococcal meningitis, and cytomegaloviral disease. These conditions are considered opportunistic infections.
When coding, be sure to note the includes:
Type 1 excludes:

 www.icd10monitor.com
www.icd10monitor.com
Coding for HIV
For inpatient coding, the physician must state the diagnosis, and if not clearly documented, there is an opportunity to query for clarification. For outpatient coding, it is often challenging for coders to determine if the patient is just HIV + (Z21) or if the patient has ever had an HIV-related illness (B20). As of now, most outpatient coders do not have the capability to query for OP coding. If the coder is unable to determine which the patient has based on the documentation provided, we should default to asymptomatic, rather than assigning the patient a diagnosis of AIDS.
Opportunistic Infections (OIs)
Healthy immune systems can be exposed to certain viruses, bacteria, or parasites and have no reaction to them. However, people living with HIV/AIDS may have serious health threats from what are known as “opportunistic infections (OIs)”. These infections attack the weakened immune system and can be life-threatening. OIs are signs of a declining immune system. Most life-threatening OIs occur when the CD4 count falls below 200 cells/mm3. The CDC developed a list of more than 20 OIs that are considered AIDS-defining conditions. Patients having laboratory-confirmed HIV infections and one or more of these OIs, will be diagnosed with AIDS regardless of the CD4 count.

 acdis.org
acdis.org

Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
AIDS is the final stage of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, stage 4 by the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria (2007) and stage 3 by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2008) criteria or clinical categories B or C (CDC). AIDS code (B20) applies if AIDS has ever been previously diagnosed. B20 must always be coded on every single subsequent encounter and never again code Z21 once AIDS is assigned.

 www.eclathealth.com
www.eclathealth.com
 www.aapc.com
www.aapc.com
Common diagnosis codes
The following charts list codes and categories of codes that carry a risk adjustment score. (HCC
weight).
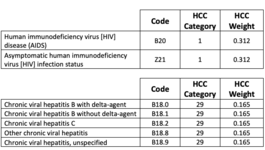
Both B20 and Z21 carry the same HCC risk score/weight.
Following ICD-10 guidelines, a patient with HIV status without symptoms is coded with Z21,
positive HIV status. Some doctors and non-physician practitioners would prefer to use B20.
According to ICD-10, B20 is used when the patient has confirmed AIDS. According to these
guidelines, if a patient has or has had an HIV related condition, use B20 AIDS. If the patient has
a positive HIV status, without symptoms or related conditions, use Z21. Both carry the same risk
adjustment score.
Report co-morbid conditions that are treated or that affect treatment
Medical practices “report” diagnoses by submitting the diagnosis on a health insurance claim
form sent to the payer for payment of a service or procedure.
Key Points
• Major depressive disorder: Use a specific code in category F32 or F33
• Diabetes: If the patient has a complication or manifestation of diabetes, such as
nephropathy, use the code with the manifestation
• Neoplasms: Report malignant neoplasm if the patient has evidence of the disease or is
receiving treatment for the disease. If neither of those are present, use personal history
of malignant neoplasm codes.
• Infectious diseases: Document other infectious diseases and submit the diagnosis codes
for them on the claim form when the patient is treated.
• Substance abuse: Report substance abuse codes if documented at the time of a visit.
1) Code only confirmed cases
Code only confirmed cases of HIV infection/illness. This is an exception
to the hospital inpatient guideline Section II, H.
In this context, “confirmation” does not require documentation of
positive serology or culture for HIV; the provider’s diagnostic statement
that the patient is HIV positive or has an HIV-related illness is sufficient.
2) Selection and sequencing of HIV codes
(a) Patient admitted for HIV-related condition
If a patient is admitted for an HIV-related condition, the principal
diagnosis should be B20, Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV]
disease followed by additional diagnosis codes for all reported
HIV-related conditions.
(b) Patient with HIV disease admitted for unrelated condition
If a patient with HIV disease is admitted for an unrelated
condition (such as a traumatic injury), the code for the unrelated
condition (e.g., the nature of injury code) should be the principal
ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding andReporting
FY 2022
Page 20 of 115
diagnosis. Other diagnoses would be B20 followed by additional
diagnosis codes for all reported HIV-related conditions.
(c) Whether the patient is newly diagnosed
Whether the patient is newly diagnosed or has had previous
admissions/encounters for HIV conditions is irrelevant to the
sequencing decision.
(d) Asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus
Z21, Asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus [HIV]
infection status, is to be applied when the patient without any
documentation of symptoms is listed as being “HIV positive,”
“known HIV,” “HIV test positive,” or similar terminology. Do
not use this code if the term “AIDS” or “HIV disease” is used or
if the patient is treated for any HIV-related illness or is described
as having any condition(s) resulting from his/her HIV positive
status; use B20 in these cases.
(e) Patients with inconclusive HIV serology
Patients with inconclusive HIV serology, but no definitive
diagnosis or manifestations of the illness, may be assigned code
R75, Inconclusive laboratory evidence of human
immunodeficiency virus [HIV].
(f) Previously diagnosed HIV-related illness
Patients with any known prior diagnosis of an HIV-related illness
should be coded to B20. Once a patient has developed an
HIV-related illness, the patient should always be assigned code
B20 on every subsequent admission/encounter. Patients
previously diagnosed with any HIV illness (B20) should never be
assigned to R75 or Z21, Asymptomatic human
immunodeficiency virus [HIV] infection status.
(g) HIV Infection in Pregnancy, Childbirth and the Puerperium
During pregnancy, childbirth or the puerperium, a patient
admitted (or presenting for a health care encounter) because of an
HIV-related illness should receive a principal diagnosis code of
O98.7-, Human immunodeficiency [HIV] disease complicating
pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium, followed by B20 and
the code(s) for the HIV-related illness(es). Codes from Chapter
15 always take sequencing priority.
Patients with asymptomatic HIV infection status admitted (or
presenting for a health care encounter) during pregnancy,
childbirth, or the puerperium should receive codes of O98.7- and
Z21.
ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding andReporting
FY 2022
Page 21 of 115
(h) Encounters for testing for HIV
If a patient is being seen to determine his/her HIV status, use
code Z11.4, Encounter for screening for human
immunodeficiency virus [HIV]. Use additional codes for any
associated high-risk behavior, if applicable.
If a patient with signs or symptoms is being seen for HIV testing,
code the signs and symptoms. An additional counseling code
Z71.7, Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] counseling, may
be used if counseling is provided during the encounter for the
test.
When a patient returns to be informed of his/her HIV test results
and the test result is negative, use code Z71.7, Human
immunodeficiency virus [HIV] counseling.
If the results are positive, see previous guidelines and assign
codes as appropriate.
(i) History of HIV managed by medication
If a patient with documented history of HIV disease is
currently managed on antiretroviral medications, assign code
B20, Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] disease. Code
Z79.899, Other long term (current) drug therapy, may be
assigned as an additional code to identify the long-term
(current) use of antiretroviral medications.
Guideline C20 A 6
6) External cause code can never be a principal diagnosis An external cause code can never be a principal (first-listed) diagnosis.
The proper sequencing for HIV depends on the reason for the admission or encounter. When a patient is admitted for an HIV-related condition, sequence B20 Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] disease first, followed by additional diagnosis codes for all reported HIV-related conditions. Conditions always considered HIV-related include Kaposi’s sarcoma, lymphoma, Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), cryptococcal meningitis, and cytomegaloviral disease. These conditions are considered opportunistic infections.
Advice for Coding and Documenting HIV
Clinical coding of HIV in ICD-10-CM brings you to Chapter 1 for Certain Infectious and Parasitic Diseases, code range A00-B99, and then to the three-character code B20, Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).When coding, be sure to note the includes:
- Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)
- AIDS-related complex (ARC)
- HIV infection, symptomatic
Type 1 excludes:
- Asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection status (Z21)
- Exposure to HIV virus (Z20.6)
- Inconclusive serologic evidence of HIV (R75
- Use Additional: Code(s) to identify all manifestations of HIV infection
- Code First: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease complicating pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium, if applicable (O98.7-)

Advice for Coding and Documenting HIV – MedLearn Publishing
National HIV Testing Day is June 27. Wednesday is National HIV Testing Day—a day designated to highlight the importance of testing in detecting, treating, and preventing human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. This special day is designed to encourage people to get tested for HIV, know...
Coding for HIV
For inpatient coding, the physician must state the diagnosis, and if not clearly documented, there is an opportunity to query for clarification. For outpatient coding, it is often challenging for coders to determine if the patient is just HIV + (Z21) or if the patient has ever had an HIV-related illness (B20). As of now, most outpatient coders do not have the capability to query for OP coding. If the coder is unable to determine which the patient has based on the documentation provided, we should default to asymptomatic, rather than assigning the patient a diagnosis of AIDS.
Opportunistic Infections (OIs)
Healthy immune systems can be exposed to certain viruses, bacteria, or parasites and have no reaction to them. However, people living with HIV/AIDS may have serious health threats from what are known as “opportunistic infections (OIs)”. These infections attack the weakened immune system and can be life-threatening. OIs are signs of a declining immune system. Most life-threatening OIs occur when the CD4 count falls below 200 cells/mm3. The CDC developed a list of more than 20 OIs that are considered AIDS-defining conditions. Patients having laboratory-confirmed HIV infections and one or more of these OIs, will be diagnosed with AIDS regardless of the CD4 count.

Q&A: Using codes Z21 and B20 for HIV patients | ACDIS
Q: I have a question about coding HIV and HIV-related illnesses. If a physician documents a patient is HIV positive, should the chart be coded to Z21? What about if they document the patient is HIV positive with an HIV-related illness—would that be coded to B20?

Clarifying Coding for HIV and AIDS in ICD-10
Tune in to this monthly online coding column, facilitated by AHIMA’s coding experts, to learn about challenging areas and documentation opportunities for ICD-10-CM/PCS.By Elena Miller, MPH, RHIA, CCSWhile many people have heard the term “HIV” before, fewer are likely to know what it stands for...
journal.ahima.org
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
AIDS is the final stage of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, stage 4 by the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria (2007) and stage 3 by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2008) criteria or clinical categories B or C (CDC). AIDS code (B20) applies if AIDS has ever been previously diagnosed. B20 must always be coded on every single subsequent encounter and never again code Z21 once AIDS is assigned.
- Documentation coded as B20 –AIDS: HIC illness, HIV disease, ARC (AIDS-related complex), HIV symptomatic (any current AIDS-defining condition), HIV currently being treated for an HIV-related illness or is described as having any condition resulting from HIV + status, Acquired immune deficiency syndrome.
- Once a patient has any HIV-related illness (OI0, every subsequent encounter should be coded as AIDS (B20)
- Asymptomatic HIV (Z21) and inclusive HIV R75) are never reported once a patient has a confirmed diagnosis of AIDS.


HIV and AIDS, Understanding the Disease and Documentation Requirements
HIV & AIDS, Understanding the Disease & Documentation Requirements.HIV & one or more of these OIs will be diagnosed with AIDS regardless of the CD4 count.

HIV: ICD-10 Dx. Coding
When a patient is admitted for an HIV-related condition, sequence B20 Human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] disease first.
Common diagnosis codes
The following charts list codes and categories of codes that carry a risk adjustment score. (HCC
weight).

Both B20 and Z21 carry the same HCC risk score/weight.
Following ICD-10 guidelines, a patient with HIV status without symptoms is coded with Z21,
positive HIV status. Some doctors and non-physician practitioners would prefer to use B20.
According to ICD-10, B20 is used when the patient has confirmed AIDS. According to these
guidelines, if a patient has or has had an HIV related condition, use B20 AIDS. If the patient has
a positive HIV status, without symptoms or related conditions, use Z21. Both carry the same risk
adjustment score.
Report co-morbid conditions that are treated or that affect treatment
Medical practices “report” diagnoses by submitting the diagnosis on a health insurance claim
form sent to the payer for payment of a service or procedure.
Key Points
• Major depressive disorder: Use a specific code in category F32 or F33
• Diabetes: If the patient has a complication or manifestation of diabetes, such as
nephropathy, use the code with the manifestation
• Neoplasms: Report malignant neoplasm if the patient has evidence of the disease or is
receiving treatment for the disease. If neither of those are present, use personal history
of malignant neoplasm codes.
• Infectious diseases: Document other infectious diseases and submit the diagnosis codes
for them on the claim form when the patient is treated.
• Substance abuse: Report substance abuse codes if documented at the time of a visit.


